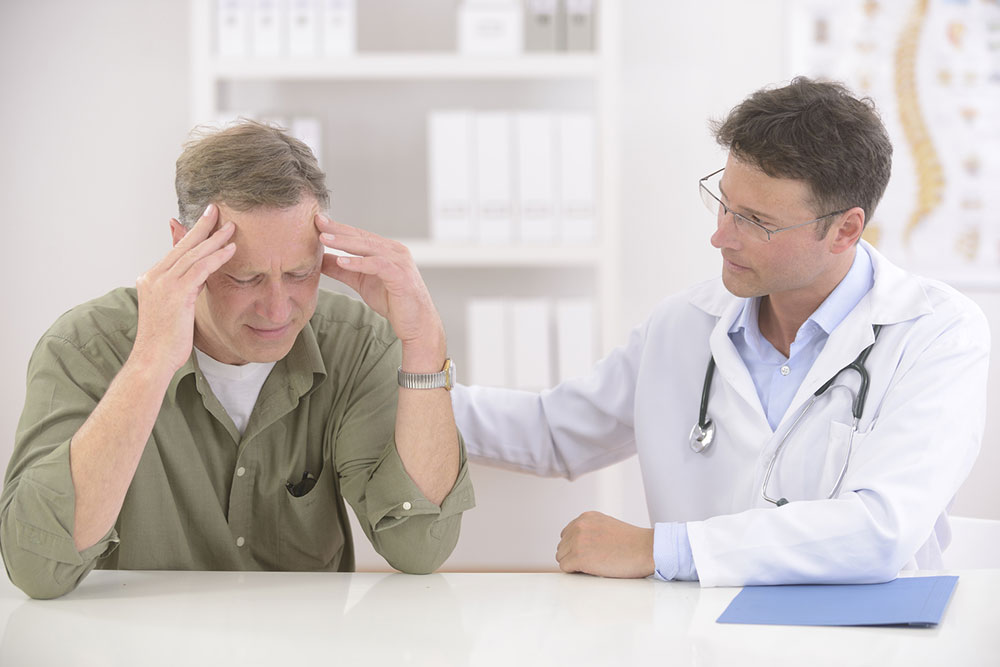
Signs and symptoms of meningitis
Depending on the age of the person and the cause of the infection, the symptoms of meningitis can vary. Sometimes symptoms begin to show almost instantly after the person has been infected and other times, it can take several days to show after the person has had a cold, nausea, diarrhea or other signs of infection. Most common symptoms include:
- Lack of energy
- Irritability
- Fever
- Headache
- Sensitivity to light
- Skin rash
- Stiff neck
Symptoms in infants with meningitis are different from those in adults. Babies with this condition tend to be cranky, sleepy or hard to wake up and do not feed properly. They are also hard to console despite every attempt that would have comforted them normally. Other symptoms that can be noticed in babies suffering from meningitis are:
- Fever
- Bulging fontanel (soft spot on the head)
- Lower than normal temperature
- Stiffness in the body and neck
- Weak sucking motion
- High pitched cry
- Jaundice (yellowish skin color)
- Cold hands and feet
- Extreme shivering
- Marks of bruises anywhere on the body
- Diarrhea
The first symptoms in toddlers are usually headache, fever, vomiting and a general feeling of being unwell. Fever is often absent in babies less than 3 months of age and even rashes do not always appear. Children below the age of 5 are at higher risk of meningitis. All the symptoms of meningitis are not always present in young children and do not appear in any order.
After toddlers, slightly older children and teenagers, are in the next most at-risk group. Along with other usual symptoms, young people tend to become extremely pale, confused, delirious, and may have fits sometimes. It is essential to trust one’s instincts and seek medical help as soon as any symptoms are noticed. Timely intervention is very important and prevents the condition from turning fatal.
The classic triad of meningitis symptoms is having a fever, headache, and a stiff neck. Generally, common symptoms are the vaguest as they could occur along with bacterial or viral infections. Specific symptoms of meningitis which are common but more noticeable in bacterial meningitis rather than viral meningitis are:
- Back pain that is caused by meningitis worsens when the leg is bent close to the chest in a fetal position. It gets better with a change in position but is present most of the time.
- Rashes are caused by a bacterial infection that results in meningitis. It leads to bleeding in tiny blood vessels caused by the spread of the infection outside the nervous system.
- Very high fever, sometimes even above 103 degrees, accompanies other symptoms.
- Meningitis is an infection affecting the nervous system leading to symptoms like poor concentration and intermittent confusion.
- In severe cases of meningitis, where infection spreads through the meninges to the brain, it causes sudden delirium, confusion, and behavioral changes.
- In rare cases, meningitis can also cause a loss of consciousness. In such a condition of coma, high-level medication helps to resolve the infection.
The symptoms of viral meningitis mostly improve in approximately 8-10 days but bacterial meningitis is usually more severe and lasts longer.