Health
An overview of melanoma
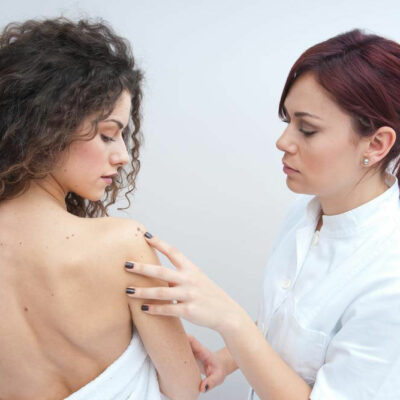
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. It affects the melanocytes, the cells in the skin that produce melanin, the pigment that gives color to the skin. Melanoma occurs when the melanocytes mutate, grow, and spread rapidly, pushing out the healthy cells in the skin. It is not as common as the other types of skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, but it is a more serious disease as it tends to metastasize. Science and technology have improved the diagnosis and treatment options for the disease, but the Center for Diseases Control (CDC) has still quoted that the number of cases has doubled over the last 30 years. Also, it is spreading faster than any other form of cancer. Cases of melanoma are seen to be rising alarmingly in people aged between 15 and 29 years. As in most cases of cancer, early detection is the key to getting cured and surviving over a substantial period of time. Melanoma on the other parts of the body Though melanoma is considered a skin cancer (cutaneous melanoma), although rarely, it can also affect the other parts of the body: Acral or acral lentiginous melanoma forms on the palms and soles or under the fingernails or toenails.
Read More